Are you a student with a passion for engineering? Have you ever considered a career in mechanical engineering? If so, then exploring the mechanical engineer career path in the USA might be the perfect opportunity for you. In this article, we will provide you with an overview of the profession, giving you all the necessary information to understand what it takes to become a successful mechanical engineer in the United States. Whether you’re fascinated by designing machines or solving complex problems, this career path offers a wide range of opportunities for growth and fulfillment. So, let’s dive in and discover the exciting world of mechanical engineering!
This image is property of static.zippia.com.
1. Education and Training
Undergraduate degree
To become a mechanical engineer in the USA, a strong educational foundation is essential. Typically, this journey begins with an undergraduate degree in mechanical engineering or a related field. During your studies, you will gain a broad understanding of the principles of mechanics, thermodynamics, materials science, and engineering design. This will provide you with the necessary knowledge to analyze and solve complex problems in the world of engineering.
Internships and co-op programs
To enhance your practical skills and gain valuable real-world experience, it is highly recommended to participate in internships and co-op programs. These opportunities allow you to apply what you have learned in the classroom to actual engineering projects. By working alongside professionals in the field, you will gain insights into the industry, develop essential technical skills, and build a network of industry contacts. Internships and co-op programs also provide a chance to explore different industries and sectors, helping you determine your career preferences.
Continuing education and professional development
The field of mechanical engineering is constantly evolving, with new technologies and advancements emerging regularly. To stay competitive in the industry, it is crucial to engage in continuous learning and professional development. This can involve attending workshops, conferences, and seminars, as well as pursuing advanced degrees or certifications. By staying updated on the latest developments in the field, you can adapt your skills and knowledge to meet the evolving demands of the industry.
2. Skills and Qualifications
Strong mathematical and analytical skills
Mechanical engineering heavily relies on mathematics and analytical thinking. As a mechanical engineer, you will need a strong foundation in calculus, differential equations, and linear algebra. These skills will enable you to analyze and solve complex engineering problems.
Problem-solving abilities
Mechanical engineers are problem solvers at heart. They possess the ability to break down complex challenges into smaller, manageable parts and come up with creative and innovative solutions. This requires critical thinking, logical reasoning, and a systematic approach to problem-solving.
Creativity and innovation
Innovation plays a significant role in the field of mechanical engineering. Engineers constantly seek new and improved ways to design, develop, and manufacture mechanical systems. By fostering creativity and embracing innovation, mechanical engineers can push the boundaries of technological advancements.
Attention to detail
Precision and attention to detail are vital traits for a mechanical engineer. The ability to meticulously analyze and evaluate designs, specifications, and measurements ensures the accuracy and efficiency of mechanical systems. Even the slightest oversight can have significant consequences, making attention to detail a critical aspect of the job.
Excellent communication skills
Communication is key in any professional setting, and mechanical engineering is no exception. As a mechanical engineer, you will need to effectively communicate complex ideas, designs, and technical information to colleagues, clients, and stakeholders. Strong written and oral communication skills will allow you to convey your ideas clearly and collaborate effectively with cross-functional teams.
Technical proficiency
Proficiency in technical skills is essential for a successful career as a mechanical engineer. This includes a deep understanding of computer-aided design (CAD) software, which is widely used in the industry for modeling and simulating mechanical systems. Additionally, familiarity with programming languages and other specialized software applications can greatly enhance your capabilities as an engineer.
Knowledge of CAD software
Computer-aided design (CAD) software is a crucial tool in the mechanical engineering field. Proficiency in CAD software such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, or CATIA allows you to create detailed 2D and 3D designs, simulate mechanical systems, and analyze their performance. The ability to effectively utilize CAD software is highly valued by employers and can greatly enhance your productivity and efficiency in the workplace.
Understanding of manufacturing processes
Mechanical engineers must have a comprehensive understanding of various manufacturing processes. This knowledge is crucial for designing products that can be manufactured efficiently and effectively. Understanding manufacturing processes such as machining, welding, casting, and 3D printing enables engineers to optimize designs for production, ensuring cost-effectiveness and quality.
Ability to work in teams
Collaboration and teamwork are integral to the field of mechanical engineering. As a mechanical engineer, you will often work alongside professionals from various disciplines, such as electrical engineers, materials scientists, and industrial designers. The ability to effectively collaborate and contribute your expertise in a team environment is essential for successful project completion.
Project management skills
Mechanical engineers are frequently involved in managing projects and ensuring their successful execution. Project management skills, including planning, organizing, and coordinating resources, are crucial for delivering projects on time and within budget. The ability to manage deadlines, budgets, and cross-functional teams is highly valued in the industry.
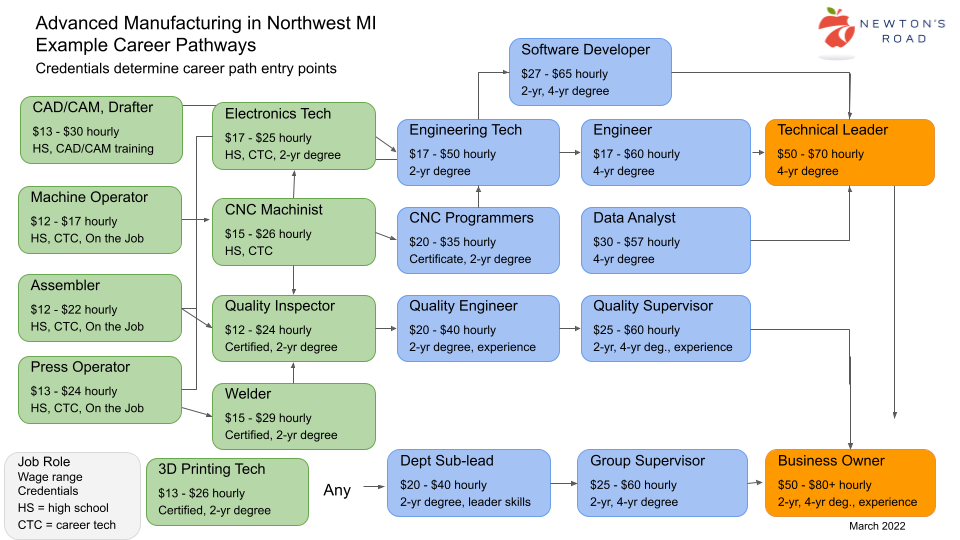
This image is property of www.nwmicareers.org.
3. Job Responsibilities
Designing and developing mechanical systems
One of the primary responsibilities of a mechanical engineer is designing and developing mechanical systems. This involves creating detailed designs, conducting feasibility studies, and selecting appropriate materials and components. Mechanical engineers must consider factors such as functionality, cost, safety, and sustainability while developing innovative and efficient mechanical systems.
Analyzing and evaluating designs
Mechanical engineers are responsible for analyzing and evaluating designs to ensure their feasibility and reliability. This involves using analytical tools and techniques to simulate and assess the performance of mechanical systems. By analyzing factors such as stress distribution, fluid flow, and heat transfer, engineers can optimize designs and identify potential areas for improvement.
Testing and troubleshooting mechanical systems
Mechanical engineers are often involved in testing and troubleshooting mechanical systems to ensure their functionality and performance. This can involve conducting experiments, collecting data, and analyzing results to identify any issues or inefficiencies. By diagnosing and resolving problems, mechanical engineers play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of mechanical systems.
Collaborating with cross-functional teams
Mechanical engineers work closely with professionals from various disciplines to develop and implement mechanical systems. This requires effective communication and collaboration with electrical engineers, software developers, project managers, and other stakeholders. By working collaboratively, engineers can leverage the expertise of different team members to create integrated and optimized solutions.
Preparing and reviewing technical reports
Mechanical engineers are responsible for preparing and reviewing technical reports to document the design, analysis, and testing of mechanical systems. These reports provide a comprehensive overview of the engineering process and form the basis for decision-making and future improvements. Clear and concise technical writing skills are essential for effectively communicating complex ideas and findings in these reports.
Estimating project costs and timelines
As part of project management responsibilities, mechanical engineers are often tasked with estimating project costs and timelines. This involves analyzing the scope of the project, evaluating resource requirements, and considering potential risks and constraints. Accurate cost and timeline estimation ensures effective project planning and resource allocation.
Ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations
Mechanical engineers must ensure that their designs and developments comply with industry standards and regulations. Compliance with standards such as ISO and ASME ensures the quality, safety, and reliability of mechanical systems. Mechanical engineers must stay up-to-date with these standards and ensure that their designs meet the necessary requirements.
Managing projects and budgets
Mechanical engineers often take on project management roles and are responsible for managing projects and budgets. This involves overseeing project timelines, coordinating resources, and monitoring progress to ensure successful project completion. Effective project management skills are crucial for delivering projects on time, within budget, and meeting client expectations.
Working with clients and stakeholders
Mechanical engineers frequently interact with clients, stakeholders, and other external parties throughout the engineering process. This includes understanding client requirements, presenting design proposals, and addressing any concerns or feedback. Building strong relationships and effectively managing client expectations are vital for successful project outcomes.
Researching and implementing new technologies
To stay at the forefront of the industry, mechanical engineers often engage in research and development of new technologies. This involves staying updated on the latest advancements, exploring innovative solutions, and implementing new technologies into mechanical systems. By embracing new technologies, mechanical engineers can drive advancements in various industries and ensure continuous improvement.
4. Industries and Sectors
Automotive industry
Mechanical engineers play a vital role in the automotive industry, contributing to the design, development, and manufacturing of automobiles. They are involved in creating efficient and innovative engine systems, chassis designs, and safety features. The automotive industry offers exciting opportunities for mechanical engineers to work on cutting-edge technologies such as electric and autonomous vehicles.
Aerospace industry
The aerospace industry relies heavily on mechanical engineers for the design and development of aircraft and spacecraft systems. Mechanical engineers contribute to the creation of propulsion systems, airframes, control systems, and aerodynamics. Working in the aerospace industry offers unique challenges and opportunities to work on groundbreaking projects that shape the future of aviation and space exploration.
Energy sector
The energy sector presents significant opportunities for mechanical engineers to contribute to the development of renewable energy sources, energy storage systems, and efficient energy utilization. Mechanical engineers are involved in designing and maintaining power generation facilities, improving energy efficiency in buildings, and developing innovative technologies such as wind turbines and solar panels.
Manufacturing industry
Mechanical engineers have a strong presence in the manufacturing industry, where they optimize manufacturing processes, design production lines, and ensure quality control. They are responsible for creating efficient and cost-effective manufacturing systems that meet industry standards. Working in the manufacturing sector allows mechanical engineers to apply their analytical skills and technical knowledge to improve productivity and quality.
Construction industry
Mechanical engineers play a crucial role in the construction industry by contributing to the design and installation of HVAC systems, plumbing systems, and fire protection systems. They ensure the efficient use of energy and resources in buildings, create sustainable infrastructure, and incorporate the latest technologies. The construction industry offers diverse opportunities for mechanical engineers to work on projects of varying scales and complexities.
Medical equipment and devices
Mechanical engineers are involved in the design and development of medical equipment and devices used in healthcare settings. They contribute to the creation of prosthetics, imaging systems, surgical instruments, and medical implants. Mechanical engineers in the medical field combine their technical skills with an understanding of human biology and biomechanics to improve patient care and enhance medical technology.
Robotics and automation
The field of robotics and automation relies heavily on mechanical engineers for the design and development of robotic systems and automated processes. Mechanical engineers contribute to creating robots for manufacturing, healthcare, exploration, and other sectors. They optimize the mechanical, control, and sensing systems to ensure efficient and safe operation. The robotics and automation industry offers exciting opportunities to work on cutting-edge technologies and contribute to the development of autonomous systems.
Consumer goods
Mechanical engineers play a significant role in the consumer goods industry, contributing to the design, development, and manufacturing of various products. From household appliances to electronic devices, mechanical engineers optimize the functionality, efficiency, and user experience of consumer goods. They ensure that products are safe, environmentally friendly, and meet consumer expectations.
Consulting firms
Mechanical engineers are often employed by consulting firms, where they provide specialized expertise and solutions to clients in various industries. Working in a consulting role allows engineers to work on a wide range of projects and collaborate with diverse clients and industries. Consulting firms offer opportunities for continuous learning, professional growth, and exposure to different engineering challenges.
Government agencies
Mechanical engineers are employed by government agencies at various levels, including federal, state, and local. They contribute to the development of public infrastructure, transportation systems, and environmental sustainability initiatives. Mechanical engineers in government agencies play a vital role in improving the quality of life for citizens by addressing engineering challenges and implementing innovative solutions.
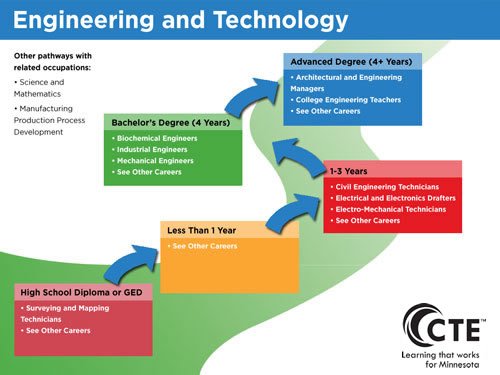
This image is property of careerwise.minnstate.edu.
5. Employment Outlook
Overall job growth for mechanical engineers
The employment outlook for mechanical engineers in the USA is positive, with steady growth projected in the coming years. As industries continue to innovate and evolve, the demand for skilled mechanical engineers remains strong. From automotive to energy and aerospace sectors, companies are seeking qualified professionals to design, develop, and enhance mechanical systems.
Opportunities in emerging industries
Emerging industries, such as renewable energy, robotics, and medical technology, offer exciting opportunities for mechanical engineers. The increasing focus on sustainability, automation, and healthcare advancements creates a demand for mechanical engineers with specialized knowledge and skills in these areas. By aligning their expertise with emerging industries, mechanical engineers can tap into new and dynamic career paths.
Demand for specialized skills
As industries become more specialized and technologically advanced, the demand for mechanical engineers with specialized skills is growing. Employers seek individuals with expertise in areas such as computational fluid dynamics, finite element analysis, robotics, and additive manufacturing. By acquiring and honing specialized skills, mechanical engineers can differentiate themselves and open doors to unique career opportunities.
Regional variations in job prospects
Job prospects for mechanical engineers can vary by region within the USA. Some states have a higher concentration of engineering firms and industries, leading to greater job opportunities. Regions with a strong focus on industries such as automotive, aerospace, and energy tend to have a higher demand for mechanical engineers. It is beneficial to consider the regional dynamics and opportunities while planning a career as a mechanical engineer.
Average salaries and benefits
Mechanical engineering offers competitive salaries and benefits. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for mechanical engineers was $88,550 in May 2020. Salaries can vary depending on factors such as experience, education, industry, and geographic location. In addition to financial rewards, mechanical engineers often enjoy benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and professional development opportunities.
6. Career Paths and Advancement
Entry-level positions
Entry-level positions are the starting point for mechanical engineering graduates. These positions provide valuable hands-on experience, allowing engineers to apply their theoretical knowledge to real-world projects. Common entry-level roles include design engineer, test engineer, and manufacturing engineer. With further experience and skill development, engineers can progress to more senior positions.
Senior mechanical engineer
Senior mechanical engineers have gained significant experience in the field and have demonstrated expertise in specific areas. They take on greater responsibilities, such as leading engineering teams, managing complex projects, and mentoring junior engineers. Senior mechanical engineers are often involved in high-level decision-making and play a crucial role in guiding the engineering direction of organizations.
Project manager
Mechanical engineers with strong project management skills may choose to pursue a career as a project manager. In this role, they oversee engineering projects from conception to completion, ensuring timely delivery, resource allocation, and budget management. Project managers collaborate with cross-functional teams, clients, and stakeholders to ensure project success.
Engineering manager
Engineering managers are responsible for overseeing the engineering department and its operations. They provide leadership, guidance, and technical expertise to engineers and ensure the efficient management of resources. Engineering managers balance technical responsibilities with organizational and strategic planning, contributing to the overall success of the engineering team and the company.
Consultant
Mechanical engineers can leverage their expertise by working as consultants. As consultants, they offer specialized knowledge and solutions to clients in various industries. Consultants may work independently or as part of consulting firms, providing engineering services, conducting feasibility studies, and advising clients on technical matters. Consulting offers diversity in projects, exposure to different industries, and the opportunity to work with a range of clients.
Research and development roles
For those passionate about innovation and pushing the boundaries of technology, research and development (R&D) roles are a rewarding career path. In R&D positions, mechanical engineers focus on developing new technologies, improving existing systems, and conducting cutting-edge research. These roles often involve collaboration with academia, industry partners, and research institutions.
Academia and teaching
Some mechanical engineers choose to pursue careers in academia and teaching. They may work as professors, lecturers, or research faculty in universities and colleges. Academic positions allow mechanical engineers to impart knowledge, conduct research, and contribute to the education of future engineers. Teaching offers the opportunity to inspire and mentor the next generation of mechanical engineers.

This image is property of s2.research.com.
7. Professional Organizations and Networks
American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)
ASME is a renowned professional organization for mechanical engineers. It provides a platform for networking, knowledge sharing, and professional development. ASME offers various resources, technical publications, and conferences that connect mechanical engineers and offer opportunities to advance their careers.
National Society of Professional Engineers (NSPE)
NSPE is a national organization that serves the interests of all professional engineers. Membership in NSPE provides access to a range of benefits, including advocacy, professional development opportunities, and networking events. NSPE promotes the highest ethical standards and helps engineers excel in their careers.
Society of Women Engineers (SWE)
SWE is a professional organization dedicated to empowering women in engineering and technology fields. It offers networking opportunities, professional development resources, and mentorship programs for women in engineering. SWE advocates for diversity and inclusion and plays a crucial role in supporting and advancing women in the engineering profession.
Engineers Without Borders (EWB)
Engineers Without Borders is an organization that facilitates engineering projects to address global challenges and improve the quality of life in underserved communities. Participating in EWB allows mechanical engineers to apply their skills and knowledge to make a positive impact internationally. EWB provides opportunities for collaboration, leadership development, and global engagement.
Local and regional engineering societies
In addition to national organizations, local and regional engineering societies offer valuable resources and networking opportunities for mechanical engineers. These societies often host events, workshops, and seminars focused on industry trends, professional development, and regional job opportunities. Joining local engineering societies can help engineers build connections and navigate the local engineering community.
8. Licensure and Certification
Becoming a licensed Professional Engineer (PE)
Obtaining a Professional Engineer (PE) license is a significant milestone for mechanical engineers. Licensure demonstrates competence and professionalism in the field of mechanical engineering. Becoming a licensed PE involves meeting specific education and experience requirements, passing the Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) exam, and completing the Principles and Practice of Engineering (PE) exam.
Certification options for specialization
In addition to licensure, there are various certification options available for mechanical engineers looking to specialize in specific areas. These certifications can enhance your credentials and demonstrate expertise in specialized fields such as energy management, robotics, or project management. Certifications such as Certified Energy Manager (CEM) or Project Management Professional (PMP) can open up new career opportunities and increase your marketability.
Exam requirements and preparation
To become a licensed Professional Engineer, engineers must pass the Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) exam and the Principles and Practice of Engineering (PE) exam. These exams assess fundamental knowledge and proficiency in engineering principles and application. Preparation for these exams often involves self-study, review courses, and practice exams. There are numerous resources available, including exam preparation books, online courses, and study guides to help engineers succeed in these exams.
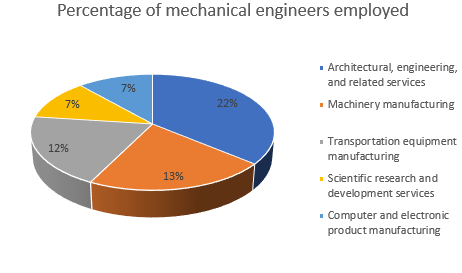
This image is property of mentr-me-prod.s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com.
9. Challenges and Opportunities
Automation and job displacement
Automation and technological advancements pose both challenges and opportunities for mechanical engineers. While automation may replace certain manual tasks, it also creates new opportunities for engineers to focus on higher-level design, analysis, and optimization. Mechanical engineers can embrace automation by leveraging their technical skills and adapting to new roles that require expertise in system integration, robotics, and artificial intelligence.
Sustainability and environmental concerns
Sustainability and environmental concerns are increasingly important in the field of mechanical engineering. Engineers are tasked with designing energy-efficient systems, reducing environmental impact, and addressing global challenges such as climate change. This presents an opportunity for engineers to contribute to a more sustainable future by developing innovative solutions, adopting renewable energy sources, and promoting eco-friendly practices.
Global competition
Globalization has led to increased competition in the engineering industry. Mechanical engineers must stay competitive by continuously expanding their knowledge and skills. Embracing lifelong learning, staying updated on trends and advancements, and pursuing professional development opportunities is crucial to succeed in a globally competitive market.
Advancements in technology
Advancements in technology, such as additive manufacturing, artificial intelligence, and simulation tools, present exciting opportunities for mechanical engineers. These new technologies provide engineers with improved capabilities for designing, prototyping, and optimizing mechanical systems. By embracing and leveraging these advancements, mechanical engineers can enhance their productivity, efficiency, and creativity.
Increasing demand for interdisciplinary skills
The engineering landscape is becoming more interdisciplinary, with collaboration among different fields becoming increasingly important. Mechanical engineers who possess interdisciplinary skills, such as understanding electrical engineering, software development, or materials science, have a competitive advantage. The ability to collaborate effectively with professionals from different disciplines is crucial in addressing complex engineering challenges.
Diversity and inclusion in the field
Diversity and inclusion in the engineering field are essential for fostering innovation, creativity, and problem-solving. Mechanical engineering has traditionally been male-dominated, but efforts are being made to promote diversity and inclusion. Encouraging underrepresented groups, such as women and minorities, to pursue careers in engineering, and creating inclusive work environments are crucial for the future of the profession.
10. Resources and References
Books and textbooks
- “Mechanical Engineering Reference Manual for the PE Exam” by Michael R. Lindeburg
- “Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design” by Richard G. Budynas and Keith J. Nisbett
- “Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer” by Theodore L. Bergman, Adrienne S. Lavine, Frank P. Incropera, David P. DeWitt
Online resources and websites
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME): www.asme.org
- National Society of Professional Engineers (NSPE): www.nspe.org
- Society of Women Engineers (SWE): www.swe.org
- Engineers Without Borders (EWB): www.ewb-usa.org
Industry publications
- Mechanical Engineering magazine by ASME
- Engineering News-Record (ENR)
- Design News
- Machine Design magazine
Professional journals and research papers
- Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics
- Journal of Engineering Mechanics
- International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer
Networking events and conferences
- ASME Annual Meeting and Exposition
- NSPE Professional Engineers Conference
- SWE Annual Conference and Career Fair
- Engineers Without Borders Regional and National Conferences
By exploring the mechanical engineer career path in the USA, you become aware of the education and training required, the skills and qualifications needed, as well as the job responsibilities involved. Additionally, you gain insight into the various industries and sectors that mechanical engineers can work in, and the employment outlook for this field. Understanding the career paths and opportunities available, as well as the challenges and resources that exist, helps you navigate your own path as a mechanical engineer and make informed decisions for your future.