Are you a student considering a career in human resources management in the USA? Look no further for an exciting glimpse into this rewarding career path. As a human resources manager, you’ll have the opportunity to make a significant impact within organizations by overseeing various aspects of employment, from recruiting and hiring to employee relations and benefits administration. This article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the career path of a human resources manager in the USA, offering valuable insights and shedding light on the potential opportunities that await you in this dynamic and evolving field.
This image is property of www.aihr.com.
1. Job Description
As a Human Resources Manager, your primary responsibility is to oversee and manage the human resources functions within an organization. This includes tasks such as recruiting, hiring, onboarding, training, and maintaining employee relations. You will play a crucial role in developing and implementing policies and procedures to ensure compliance with employment laws and create a positive work environment. Additionally, you will be responsible for handling employee benefits, compensation, and performance evaluations.
Education and qualifications
To become a Human Resources Manager, a bachelor’s degree in human resources, business administration, or a related field is typically required. Some employers may prefer candidates with a master’s degree, especially for more senior positions. It is also beneficial to have relevant work experience in human resources or a related field.
Skills and competencies
Being a successful Human Resources Manager requires a combination of skills and competencies. Strong interpersonal and communication skills are essential as you will be interacting with employees at all levels of the organization. You should have excellent problem-solving skills and the ability to make quick and effective decisions. Analytical skills are also important, as you will need to analyze data and make data-driven decisions. Additionally, you should be well-versed in employment laws and regulations and have good organizational and time management skills.
Responsibilities and tasks
Your responsibilities as a Human Resources Manager will vary depending on the organization you work for, but they generally include:
- Developing and implementing HR policies and procedures
- Recruiting and hiring new employees
- Conducting orientation and onboarding programs
- Managing employee benefits and compensation
- Handling employee relations and resolving conflicts
- Overseeing performance evaluations and implementing employee development programs
- Managing disciplinary actions and terminations
- Ensuring compliance with employment laws and regulations
- Keeping up to date with industry trends and best practices in HR management.
2. Salary and Benefits
Average salary
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for human resources managers in the United States in 2020 was $121,220. However, the salary can vary depending on factors such as location, industry, years of experience, and the size of the organization.
Benefits and perks
In addition to the competitive salary, Human Resources Managers may also receive a range of benefits and perks. These can include healthcare insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, bonuses, and professional development opportunities. Some organizations may also offer flexible work schedules, remote work options, and employee discounts.
This image is property of www.aihr.com.
3. Job Outlook
Industry growth
The demand for skilled Human Resources Managers is expected to grow as organizations increasingly recognize the importance of effective HR management. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of human resources managers is projected to grow 6 percent from 2019 to 2029, faster than the average for all occupations. This growth can be attributed to factors such as evolving employment laws, the need for organizations to attract and retain top talent, and the increasing focus on workplace diversity and inclusion.
Demand for HR managers
As businesses continue to expand, there will be a growing need for HR managers to handle the recruitment, retention, and management of employees. HR managers play a vital role in ensuring organizations have a skilled and motivated workforce. They are responsible for implementing strategies to attract and retain talented individuals, manage employee benefits and compensation, and create a positive work environment. With the increasing complexity of employment laws and the need for organizations to adapt to changing business landscapes, the demand for HR managers is expected to remain strong.
4. Education and Training
Degree requirements
To pursue a career as a Human Resources Manager, a bachelor’s degree in human resources, business administration, or a related field is generally required. Some organizations may prefer candidates with a master’s degree, especially for more senior positions. Coursework in subjects such as human resources management, organizational behavior, labor laws, and employment relations can provide a strong foundation for a career in HR.
Specializations and certifications
While not required, obtaining certifications can enhance your credentials and demonstrate your expertise in specific areas of HR management. Professional associations such as the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) offer certifications such as the SHRM Certified Professional (SHRM-CP) and SHRM Senior Certified Professional (SHRM-SCP). These certifications require passing an exam and demonstrating a certain level of experience and knowledge in HR management.
Continuing education
As the field of HR management continues to evolve, continuous learning is crucial to stay updated with the latest trends and best practices. Participating in workshops, seminars, and conferences can provide opportunities to expand your knowledge and network with other HR professionals. Additionally, reading industry publications and joining professional HR associations can help you stay informed about the latest developments in the field.
This image is property of www.aihr.com.
5. Skills and Competencies
Interpersonal skills
Effective interpersonal skills are essential for HR managers as they interact with employees at all levels of the organization. You should be able to build rapport, listen actively, and communicate clearly with employees, managers, and external stakeholders. Being approachable, empathetic, and having strong conflict resolution skills can contribute to creating a positive work environment.
Problem-solving skills
HR managers often encounter challenges and problems that require effective problem-solving skills. You should be able to gather relevant information, analyze data, and make informed decisions. Having the ability to think critically, evaluate alternatives, and propose creative solutions can contribute to resolving HR issues in a timely and efficient manner.
Analytical skills
As an HR manager, you will often work with data and analyze various metrics to make data-driven decisions. Strong analytical skills can help you identify trends, detect areas for improvement, and make strategic recommendations. Proficiency in using HR software and tools for data analysis is also essential in today’s data-driven business environment.
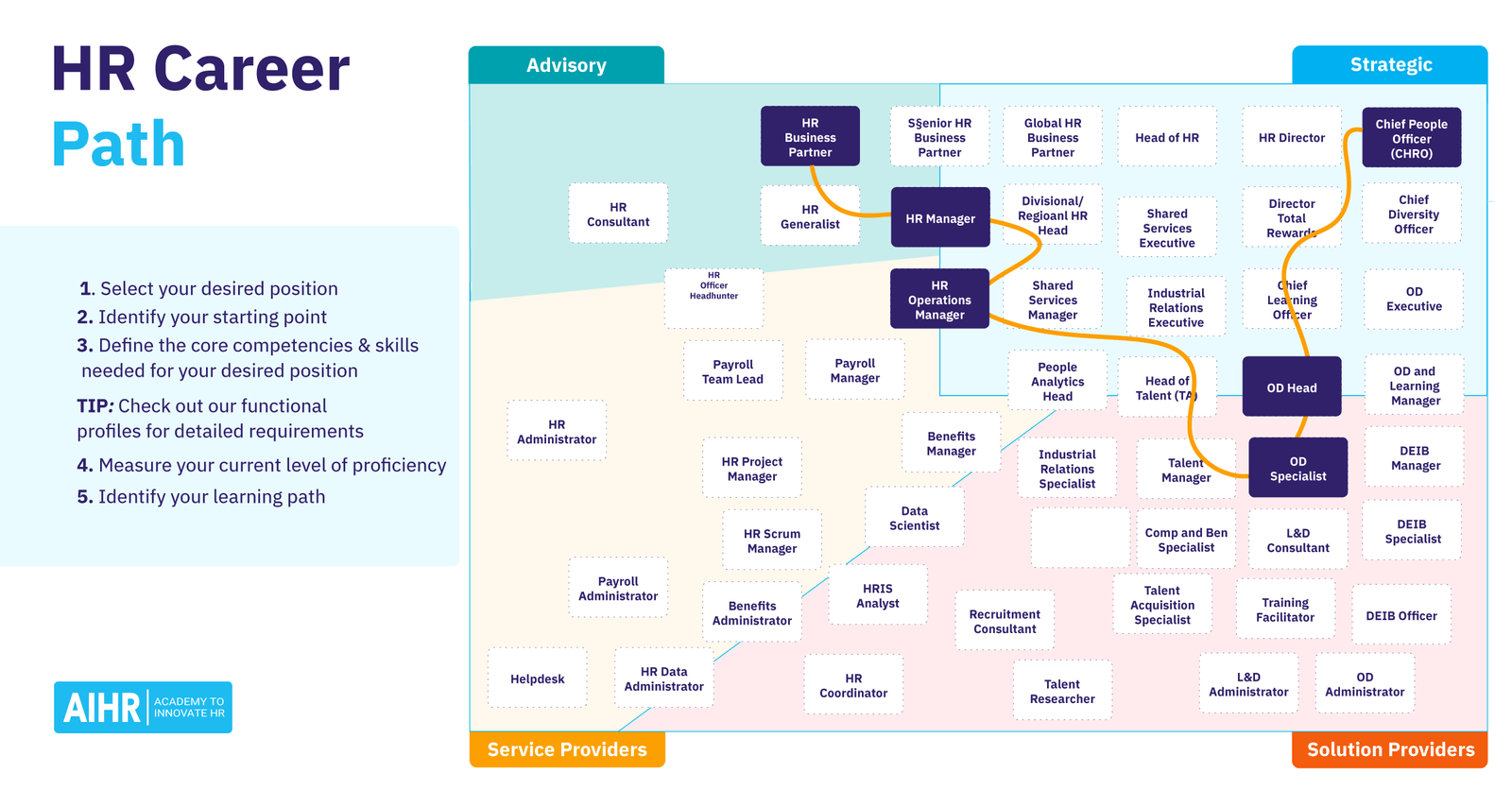
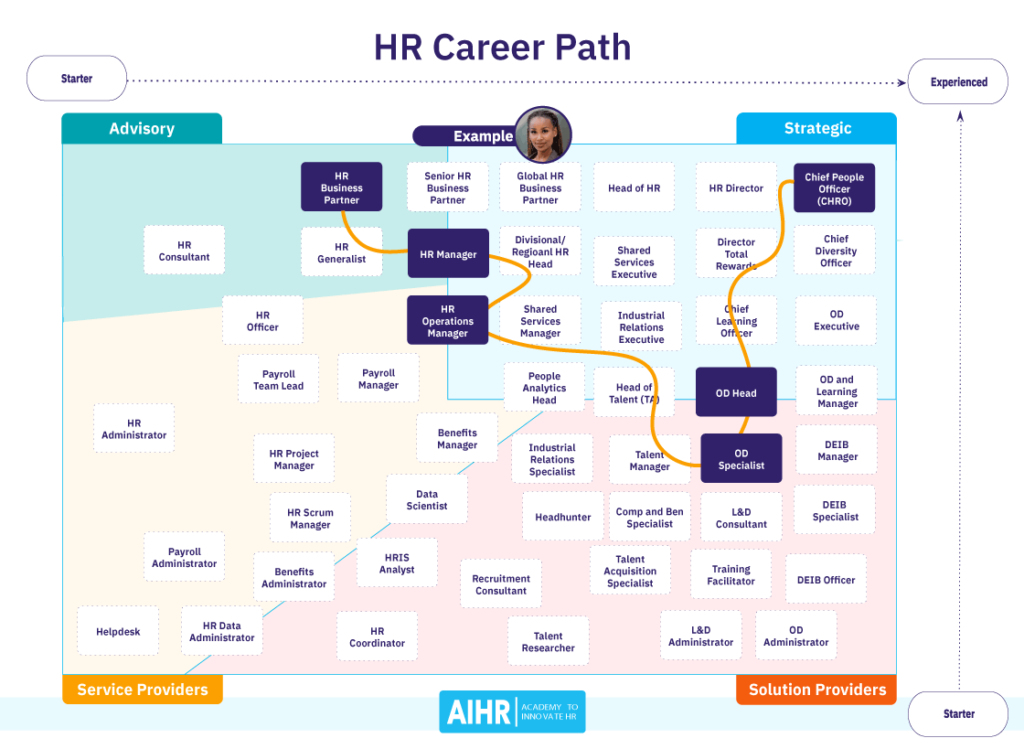
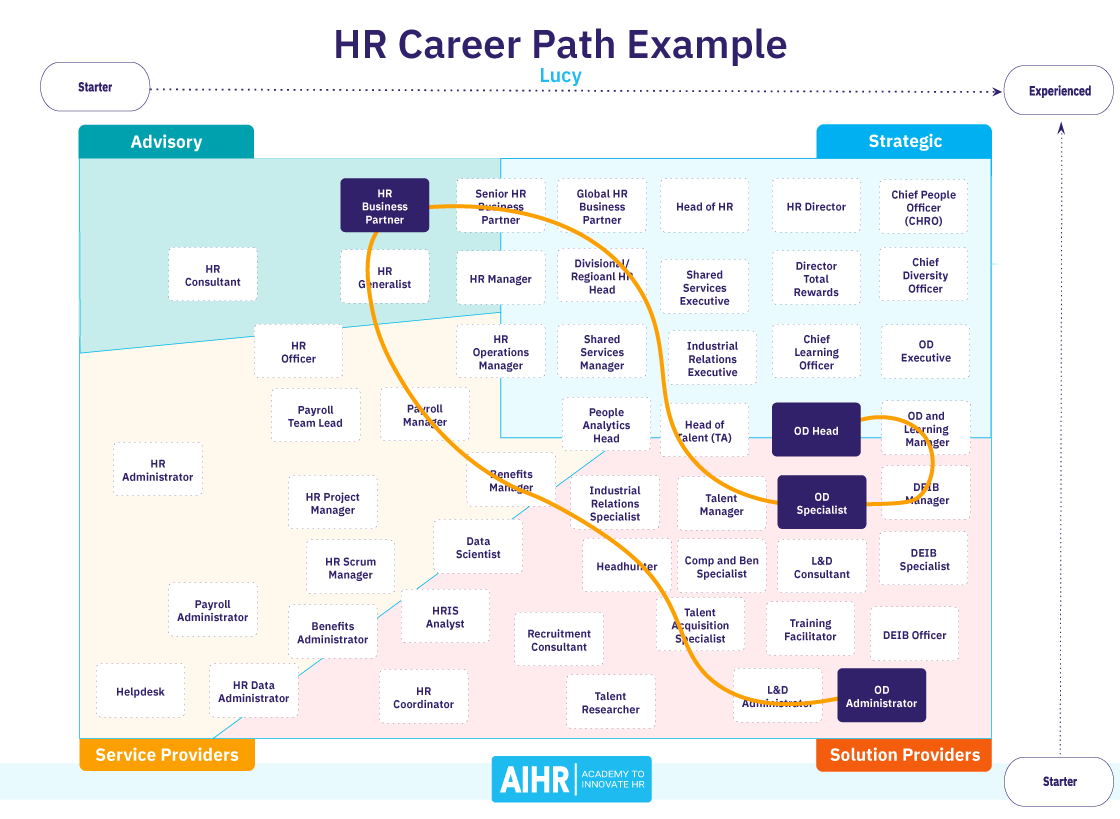
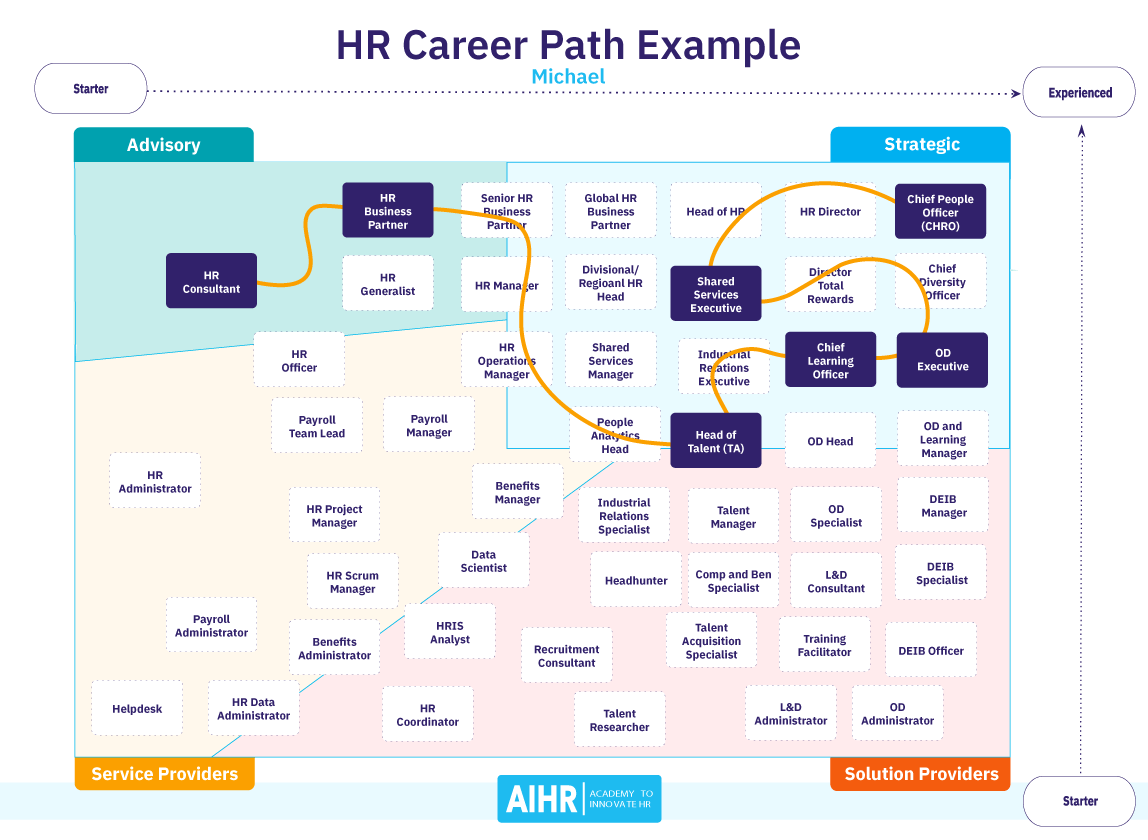
6. Advancement and Career Progression
Entry-level positions
Most individuals start their HR career in entry-level positions such as HR assistants, coordinators, or recruiters. In these roles, you will have the opportunity to learn about various HR functions and gain practical experience. It is common to gradually take on more responsibilities and move up the career ladder.
Mid-level positions
After gaining experience and demonstrating competency in HR functions, you can progress to mid-level positions such as HR generalist or HR specialist. In these roles, you will have a broader scope of responsibilities and may be responsible for specific HR functions such as employee relations, talent acquisition, or compensation and benefits.
Executive-level positions
With years of experience and a track record of success, you can advance to executive-level positions such as HR manager, HR director, or vice president of human resources. In these roles, you will be responsible for strategic planning, overseeing HR operations, and collaborating with senior leadership to align HR policies and practices with organizational goals.
Alternate career paths
While many HR professionals choose to advance within the HR field, there are also opportunities to transfer skills to other roles within the organization. HR skills such as communication, problem-solving, and strategic thinking are highly transferable and can open doors to other areas such as organizational development, training and development, or management consulting.
This image is property of www.aihr.com.
7. Industries and Sectors
HR in corporate sector
Human Resources Managers play a vital role in the corporate sector, ensuring that organizations have the right talent and resources to achieve their goals. In corporate settings, HR managers are responsible for talent acquisition, employee development, performance management, and employee relations. They work closely with executives and department heads to align HR strategies with business objectives and drive organizational success.
HR in nonprofit organizations
In nonprofit organizations, HR managers face unique challenges related to budget constraints and the need to attract and retain dedicated staff. HR managers in this sector often handle a wide range of responsibilities, including recruitment, compensation and benefits, employee engagement, and compliance with laws and regulations that pertain to nonprofits. They play a crucial role in supporting the mission of the organization while maintaining a positive work environment.
HR in government sector
Human Resources Managers in the government sector are responsible for managing HR functions within government agencies at various levels. They handle talent acquisition, employee relations, performance management, and compliance with governmental regulations. HR managers in this sector often play a critical role in shaping and implementing policies that impact the workforce.
HR in healthcare industry
In the healthcare industry, HR managers face unique challenges related to workforce management, regulatory compliance, and employee well-being. They are responsible for ensuring the organization has a qualified and engaged healthcare workforce, managing compensation and benefits specific to the industry, and navigating the complex healthcare regulatory environment. HR managers in this sector play a vital role in supporting the mission of healthcare organizations while addressing the unique needs of the healthcare workforce.
8. Work Environment
Office setting
Human Resources Managers typically work in an office setting, often within the HR department or in close proximity to other departments. They may have their own office or share a workspace. The work environment is generally professional and may involve interacting with employees, managers, and external stakeholders throughout the day.
Work hours
The typical work hours for HR managers are usually full-time, with standard business hours of Monday to Friday. However, depending on the organization and specific roles and responsibilities, HR managers may occasionally need to work extended hours or be available outside of regular business hours to handle employee issues or urgent matters.
Travel requirements
The amount of travel required for Human Resources Managers can vary depending on the organization and its geographic reach. In some cases, HR managers may need to travel to other locations to conduct interviews, attend meetings or training sessions, or provide support to remote offices or branches. However, travel requirements are generally minimal compared to other professions.
This image is property of www.aihr.com.
9. Challenges and Rewards
Challenges faced by HR managers
Human Resources Managers face a variety of challenges in their roles. Some common challenges include:
- Balancing employee needs with organizational goals
- Addressing employee conflicts and managing difficult situations
- Staying up to date with changing employment laws and regulations
- Managing cultural diversity and promoting inclusion in the workplace
- Handling sensitive employee issues such as layoffs or terminations.
Rewards and job satisfaction
While the role of an HR manager can be challenging, it also offers many rewards and opportunities for job satisfaction. Some rewards of being an HR manager include:
- Making a positive impact on employees’ lives and career development
- Contributing to the success and growth of the organization
- Building strong relationships with employees and management
- Continuous learning and professional development opportunities
- Having a diverse and dynamic work environment.
11. Future Trends and Technologies
Impact of automation and AI
The HR field is evolving with the emergence of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. Automation can streamline HR processes such as recruitment, employee onboarding, and benefits administration, freeing up HR managers to focus on strategic initiatives. AI-powered tools can assist in candidate screening, data analysis, and even provide personalized employee training. While these technologies can enhance efficiency and productivity, HR managers will need to adapt and acquire the necessary skills to leverage these tools effectively.
Use of HR software
HR managers increasingly rely on HR software platforms for managing various HR functions. These software solutions can assist in areas such as payroll and benefits administration, performance management, employee engagement, and data analytics. As technology continues to advance, HR managers should stay informed about new software solutions and adapt to changing HR technology trends to optimize their HR operations.
Changing HR role in a digital world
The digital era is transforming the role of HR managers. HR managers are now expected to be strategic partners who contribute to the overall business strategy. They must understand how technology impacts the workforce and leverage digital tools to attract, engage, and retain top talent. Additionally, HR managers will play a crucial role in ensuring data privacy and cybersecurity within the HR function as technology continues to evolve. Embracing digital transformation and developing digital leadership skills will be essential for HR managers to thrive in the future.