Are you considering a career in the field of pharmacy in the USA? If so, you’ve come to the right place. This article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the pharmacist career path in the United States. Whether you’re a current student or someone looking to switch careers, we will explore the various aspects of this profession, including educational requirements, job outlook, and potential salary. So, if you’re ready to embark on a journey into the world of pharmacy, let’s delve into the exciting possibilities that await you!
This image is property of www.myhealthcareer.com.au.
Pharmacist Career Overview
Pharmacy is a diverse and rewarding field that offers numerous opportunities for those interested in healthcare. As a pharmacist, you play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and effective use of medications. Your expertise and knowledge of pharmaceuticals allow you to make a positive impact on patient outcomes and contribute to public health. From dispensing medications to providing medication counseling, a pharmacist’s responsibilities are extensive and require a high level of professionalism and attention to detail.
Job Description
In a nutshell, the primary role of a pharmacist is to dispense medications prescribed by healthcare professionals. This involves interpreting prescriptions, ensuring the accuracy of dosage and instructions, and providing information to patients on how to take their medications safely and effectively. Pharmacists also play a vital role in monitoring drug interactions and collaborating with other healthcare professionals to optimize patient care. In addition to these responsibilities, pharmacists may engage in medication therapy management, manage pharmacy operations, and contribute to research and education.

This image is property of college.mayo.edu.
Salary Range
The salary of a pharmacist can vary depending on factors such as experience, setting, and geographical location. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, as of May 2020, the median annual wage for pharmacists in the United States was $128,710. However, the salary range for pharmacists can be anywhere from $87,790 to $162,900 or more. Factors such as specialization, additional certifications, and advanced degrees can also impact earning potential.
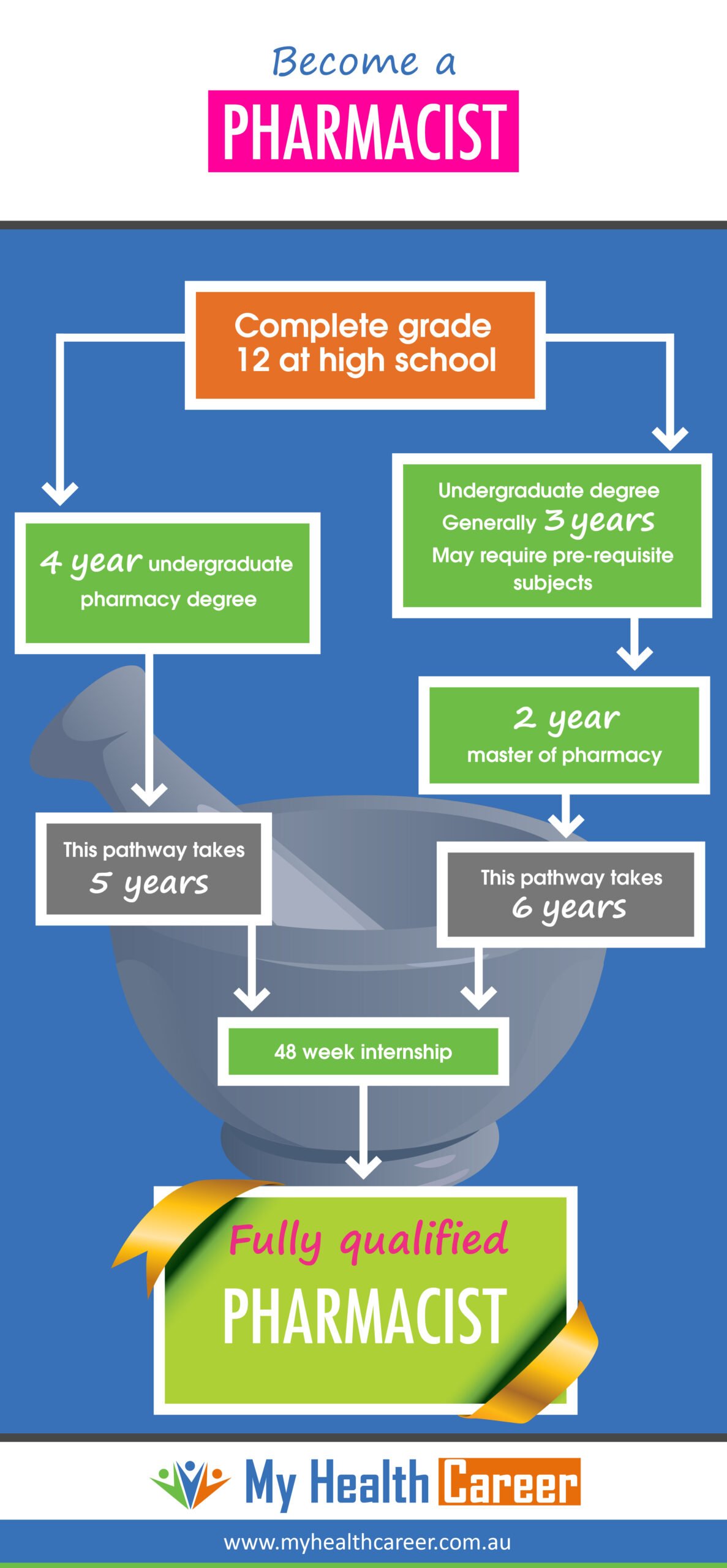
Required Education and Training
To become a pharmacist in the United States, you must complete a Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.) program. However, this requires certain prerequisites that must be fulfilled during your undergraduate studies. The first step is to earn a Bachelor’s degree, preferably in a science-related field, although it is not always a requirement. Gaining a solid foundation in subjects such as biology, chemistry, and physics is beneficial in preparing for the Pharm.D. program.

This image is property of www.ajpe.org.
Licensing and Certification
Once you have completed your Pharm.D. program, you must obtain a state license to practice pharmacy. The licensing requirements vary by state, but typically involve passing the North American Pharmacist Licensure Examination (NAPLEX) and the Multistate Pharmacy Jurisprudence Examination (MPJE). These exams assess your knowledge and understanding of pharmacy practice and laws to ensure that you are competent to practice as a pharmacist.
Professional Skills
To excel in a career as a pharmacist, certain professional skills are essential. First and foremost, having a strong foundation of pharmaceutical knowledge is crucial. Pharmacists must stay current with the latest developments in medications and treatment guidelines to provide accurate and up-to-date information to patients. Attention to detail is also critical in ensuring the accuracy of prescriptions and preventing medication errors. Effective communication and interpersonal skills are necessary to interact with patients, healthcare professionals, and other members of the pharmacy team. Furthermore, ethics, professionalism, analytical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and organization and time management skills are all important qualities for a successful pharmacist.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Work Environment
Pharmacists work in various settings, including hospitals, retail pharmacies, mail-order pharmacies, clinical research organizations, pharmaceutical companies, long-term care facilities, government agencies, home infusion pharmacies, managed care organizations, and specialty pharmacies. Each work environment offers unique challenges and opportunities. For example, hospital pharmacists collaborate closely with healthcare professionals to provide patient care, while pharmacists in retail settings interact directly with customers and provide counseling on medications and health-related issues. The work environment of a pharmacist can significantly influence daily tasks and workflow.
Advancement Opportunities
In addition to the inherent rewards of being a pharmacist, there are numerous advancement opportunities within the field. Continuing education and acquiring additional certifications or advanced degrees can open doors to specialized roles and increased responsibilities. Pharmacists can pursue specializations such as clinical pharmacy, pharmaceutical industry, pharmacy informatics, pharmacology research, pharmacy administration, geriatric pharmacy, oncology pharmacy, and pediatric pharmacy. Furthermore, leadership positions within a pharmacy department or organization offer opportunities for career growth and professional development.

This image is property of cdn.ymaws.com.
Job Outlook
The job outlook for pharmacists in the United States is positive. The demand for pharmacy services is expected to grow due to factors such as a growing elderly population and increased chronic disease prevalence. Pharmacists are essential in managing medication therapy and improving patient outcomes. Additionally, innovations in healthcare technology and the expansion of healthcare services contribute to an increased demand for pharmacists. As the role of pharmacists expands beyond traditional duties, their expertise and knowledge are increasingly valued in the healthcare industry.
Job Satisfaction
Pharmacy is a rewarding profession that provides job satisfaction in various aspects. The ability to help patients and make a positive impact on their health outcomes is a significant source of satisfaction for pharmacists. Furthermore, the knowledge that their expertise contributes to public health and the well-being of their communities provides a sense of fulfillment. Job stability and security are also notable factors contributing to job satisfaction in the pharmacy profession. With an aging population and the continuous need for medication management, the demand for pharmacists is likely to remain strong.
Challenges and Rewards
Like any profession, being a pharmacist comes with its own set of challenges and rewards. One of the challenges pharmacists face is a high workload in fast-paced environments. Dispensing medications accurately and efficiently while managing other responsibilities can be demanding. Dealing with insurance companies and prior authorizations can also be time-consuming and frustrating. Additionally, pharmacists have legal and ethical responsibilities, ensuring patient safety and compliance with regulations. Keeping up with changing treatment guidelines and staying current with new medications and therapies requires continuous learning and dedication.
Despite the challenges, there are numerous rewards in the field of pharmacy. Making a positive impact on patient outcomes and contributing to public health is immensely fulfilling. The stability and job security that come with the profession provide peace of mind. The opportunity for specialization and clinical practice allows pharmacists to focus on areas of interest and expand their knowledge and skills. Professional recognition and respect from colleagues and patients further enhance job satisfaction. Additionally, pharmacists often have the flexibility of choosing from a variety of work schedules, making it easier to manage work-life balance.
Steps to Become a Pharmacist
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of the pharmacist career path, let’s take a look at the essential steps to become a pharmacist in the United States:
Earn a Bachelor’s Degree
The first step on your journey to becoming a pharmacist is to earn a Bachelor’s degree. Although not always a requirement, having a degree in a science-related field can provide a solid foundation for your future studies in pharmacy.
Complete Pre-Pharmacy Coursework
During your undergraduate studies, you will need to complete specific prerequisite coursework to prepare for admission to a Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.) program. Courses in biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics are generally required. It is important to check the requirements of the Pharm.D. programs you are interested in and ensure that you fulfill all the prerequisites.
Apply to Pharm.D. Program
Once you have completed your undergraduate degree and prerequisite coursework, you can apply to accredited Pharm.D. programs. These programs typically require a separate application process, including submission of transcripts, letters of recommendation, and a personal statement. Admission to Pharm.D. programs can be competitive, so it is important to carefully review the requirements and submit a strong application.
Complete Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.) Program
The Pharm.D. program typically takes four years to complete and includes both classroom and experiential learning. During your Pharm.D. program, you will study a wide range of topics, including pharmacology, pharmacy law, therapeutics, and patient care. The program will provide you with the knowledge and skills necessary to practice as a pharmacist.
Take and Pass the NAPLEX and MPJE Exams
Upon graduation from a Pharm.D. program, you will need to take and pass the North American Pharmacist Licensure Examination (NAPLEX) and the Multistate Pharmacy Jurisprudence Examination (MPJE). The NAPLEX assesses your knowledge and understanding of pharmacy practice, while the MPJE tests your knowledge of pharmacy laws and regulations specific to the state in which you plan to practice.
Obtain State Licensure
After successfully passing the NAPLEX and MPJE exams, you can apply for state licensure. The requirements for licensure vary by state, but typically involve submitting an application, providing proof of your education and exam scores, and paying the necessary fees. It is important to familiarize yourself with the specific requirements of the state in which you plan to practice.
Consider Optional Post-Doctoral Training or Residency
While not required, many pharmacists choose to pursue post-doctoral training or residency programs to further specialize in a particular area of pharmacy practice. These programs provide additional hands-on experience and advanced training in a specific practice setting, such as a hospital or ambulatory care. Completing a residency can enhance your career prospects and open doors to specialized positions and leadership roles.
Specializations in Pharmacy
Pharmacy offers a wide range of specializations that allow pharmacists to focus on specific areas of interest and expertise. Here are some of the specializations within the field of pharmacy:
Clinical Pharmacy
Clinical pharmacists work directly with patients and healthcare teams to optimize medication therapy. They are involved in patient care, conducting medication reviews, providing drug information, and monitoring for adverse drug reactions and interactions. Clinical pharmacists often work in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmacists working in the pharmaceutical industry are involved in various aspects of drug development, manufacturing, and marketing. They may work in research and development, quality assurance, regulatory affairs, or pharmacovigilance. Pharmaceutical industry pharmacists play a critical role in ensuring drug safety and efficacy.
Retail Community Pharmacy
Retail community pharmacists work in community pharmacies, providing medication dispensing services and medication counseling to patients. They also offer advice on over-the-counter medications, health conditions, and general wellness. Retail community pharmacists play a vital role in community healthcare, promoting safe and effective medication use.
Nuclear Pharmacy
Nuclear pharmacists specialize in the preparation and dispensing of radioactive drugs used in nuclear medicine procedures. They ensure the safe handling and administration of these medications and work closely with nuclear medicine physicians and technologists. Nuclear pharmacists must adhere to strict safety protocols and regulations.
Pharmacy Informatics
Pharmacy informatics combines pharmacy practice with information technology to improve medication management systems and enhance patient care. Pharmacists in this specialization utilize technology and data analysis to optimize medication use and streamline processes. They may work in healthcare organizations or software development companies.
Pharmacology Research
Pharmacology research pharmacists focus on conducting clinical trials and studies to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of medications. They work in collaboration with researchers, physicians, and other healthcare professionals to gather data and analyze results. Pharmacology research pharmacists play a vital role in advancing pharmaceutical knowledge and improving patient care.
Pharmacy Administration
Pharmacy administrators are responsible for managing the operations of a pharmacy department or organization. They oversee budgets, staffing, regulatory compliance, and strategic planning. Pharmacy administrators often work in healthcare systems, hospitals, or government agencies.
Geriatric Pharmacy
Geriatric pharmacists specialize in providing pharmaceutical care to older adults. They have expertise in managing medications for the elderly, who often have complex medication regimens and multiple chronic conditions. Geriatric pharmacists work in various settings, including long-term care facilities, community pharmacies, and geriatric clinics.
Oncology Pharmacy
Oncology pharmacists play a critical role in the treatment and management of cancer patients. They are involved in the preparation and dispensing of chemotherapy medications, as well as providing medication counseling and managing treatment-related side effects. Oncology pharmacists work in hospitals, cancer centers, and specialized oncology clinics.
Pediatric Pharmacy
Pediatric pharmacists specialize in providing pharmaceutical care to children. They have expertise in pediatric medications, dosing, and formulation. Pediatric pharmacists work closely with pediatricians and other healthcare professionals to ensure safe and effective medication use in children. They may work in pediatric hospitals, clinics, or ambulatory care settings.
Work Settings for Pharmacists
Pharmacists have the opportunity to work in a variety of settings, depending on their interests and career goals. Here are some of the common work settings for pharmacists:
Hospital Pharmacies
Hospital pharmacists play a crucial role in providing medication management services to hospitalized patients. They work closely with healthcare teams to ensure the safe and effective use of medications. Hospital pharmacies can be high-paced environments, requiring pharmacists to be knowledgeable in various therapeutic areas.
Retail Pharmacies
Retail pharmacies, also known as community pharmacies, are typically located within drugstores or supermarkets. Retail pharmacists interact directly with patients and provide medication dispensing services and counseling. They also offer over-the-counter medication recommendations and general health advice.
Mail Order Pharmacies
Mail order pharmacies fulfill prescription orders remotely and deliver medications directly to patients’ homes. Pharmacists working in mail order pharmacies are responsible for processing prescriptions, ensuring accuracy, and providing counseling over the phone or through video consultations.
Clinical Research Organizations
Clinical research organizations (CROs) conduct research studies and clinical trials on behalf of pharmaceutical companies. Pharmacists working in CROs play an important role in monitoring and managing study medications, ensuring compliance with study protocols, and collecting and analyzing data.
Pharmaceutical Companies
Pharmaceutical companies employ pharmacists in various roles, including research and development, regulatory affairs, medical affairs, and drug safety. Pharmacists in pharmaceutical companies contribute to drug discovery, development, and post-marketing activities.
Long-Term Care Facilities
Pharmacists working in long-term care facilities, such as nursing homes or assisted living facilities, provide medication management services to residents. They ensure proper medication administration, monitor for drug interactions and adverse effects, and collaborate with healthcare teams to optimize patient care.
Government Agencies
Government agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), employ pharmacists in roles related to regulatory compliance, drug safety, public health, and policy development. Pharmacists in government agencies contribute to protecting the health and well-being of the population.
Home Infusion Pharmacies
Home infusion pharmacies provide intravenous medications and other specialized therapies to patients in their homes. Pharmacists in home infusion settings work closely with healthcare teams to prepare, deliver, and monitor the administration of infusion therapies. They ensure patients receive the appropriate medications and support their safe use at home.
Managed Care Organizations
Managed care organizations are responsible for managing healthcare services and costs for a specific population. Pharmacists in managed care organizations contribute to formulary management, medication benefit design, medication therapy management, and patient education. They play a role in ensuring cost-effective and evidence-based medication use.
Specialty Pharmacies
Specialty pharmacies specialize in providing medications and services for patients with complex, chronic, or rare conditions. Pharmacists in specialty pharmacies have expertise in specific disease states or therapeutic areas and coordinate the delivery and management of specialized medications.
Skills and Qualities for Pharmacists
To succeed as a pharmacist, certain skills and qualities are essential. Here are some of the skills and qualities that are highly valued in the field:
Pharmaceutical Knowledge
Having a strong foundation of pharmaceutical knowledge is crucial for pharmacists. They must stay up-to-date with the latest advancements in medications, therapeutic guidelines, and treatment options. Pharmacists need to understand the mechanism of action, side effects, dosing, and drug interactions of various medications to provide accurate information to patients and healthcare professionals.
Attention to Detail
Pharmacists must pay close attention to detail to ensure the accuracy of prescriptions and medication orders. A small error or oversight can have significant consequences for patient safety. Pharmacists must carefully review prescriptions, verify medication doses, and double-check for any potential drug interactions or contraindications.
Communication and Interpersonal Skills
Effective communication and interpersonal skills are essential for pharmacists, as they interact with patients, healthcare professionals, and other members of the pharmacy team on a daily basis. Pharmacists must be able to listen attentively, ask relevant questions, and communicate information in a clear and understandable manner. They need to be empathetic, approachable, and able to build trust with patients.
Ethics and Professionalism
Pharmacists are entrusted with the responsibility of ensuring patient safety and the appropriate use of medications. They must adhere to a strict code of ethics, including maintaining patient confidentiality and avoiding conflicts of interest. Professionalism is also crucial, as pharmacists are considered healthcare professionals and must conduct themselves in a manner that aligns with professional standards and expectations.
Analytical Thinking
Pharmacists need strong analytical thinking skills to assess and interpret patient-specific information, such as medical history, laboratory results, and medication profiles. They must be able to critically evaluate data and make evidence-based decisions. Analytical thinking also comes into play when identifying potential drug interactions or medication-related problems.
Problem-Solving Abilities
Pharmacists are often faced with complex medication-related problems and must be able to think critically and solve them effectively. This can involve evaluating alternative treatment options, considering patient-specific factors, and collaborating with healthcare teams to develop appropriate solutions. Problem-solving abilities are crucial in optimizing patient outcomes and ensuring safe medication use.
Organization and Time Management
Pharmacists have numerous responsibilities and must manage their time and tasks efficiently. They must be able to prioritize their workload, handle multiple tasks simultaneously, and ensure that medications are dispensed accurately and in a timely manner. Organization skills are essential in maintaining patient records, inventory management, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Patient Care and Counseling
Pharmacists play a vital role in patient care and counseling. They must be able to effectively communicate with patients about their medications, including proper administration, potential side effects, and precautions. Pharmacists should be able to address patient questions or concerns and provide accurate, evidence-based information to promote understanding and adherence to prescribed therapies.
Leadership and Teamwork
Pharmacists often work as part of a healthcare team, collaborating with physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. They must possess strong teamwork skills and be able to contribute their expertise while respecting the contributions of others. Leadership skills are also valuable, as pharmacists may lead pharmacy departments, manage pharmacy staff, or participate in quality improvement initiatives.
Continuous Learning
The field of pharmacy is constantly evolving, with new medications, treatment guidelines, and technologies emerging. Pharmacists must be committed to lifelong learning and staying abreast of advancements in the field. They should be proactive in seeking out opportunities for professional development, attending conferences, and staying informed about the latest research and evidence-based practices.
Pharmacist Job Responsibilities
As a pharmacist, you will have a wide range of responsibilities that contribute to the safe and effective use of medications. Here are some of the key job responsibilities of a pharmacist:
Dispensing Medications
The primary responsibility of a pharmacist is to accurately dispense medications prescribed by healthcare professionals. Pharmacists interpret prescriptions, select the appropriate medication and dosage form, and ensure that patients receive the correct medications.
Ensuring Accuracy of Prescriptions
Pharmacists are responsible for ensuring the accuracy of prescriptions, including verifying the medication, dosage, and instructions. They also need to review patient medication profiles to identify any potential drug interactions, allergies, or contraindications.
Providing Medication Counseling
Pharmacists play a critical role in providing medication counseling to patients. They educate patients about their medications, including proper administration techniques, potential side effects, and precautions. Pharmacists address patient questions or concerns and provide clear and understandable instructions.
Monitoring Drug Interactions
Pharmacists monitor for potential drug interactions between different medications that patients may be taking. They assess the compatibility of medications and advise patients and healthcare professionals on any necessary adjustments to ensure safe and effective medication use.
Collaborating with Healthcare Professionals
Pharmacists collaborate closely with physicians, nurses, and other healthcare professionals as part of a multidisciplinary team. They provide input and expertise regarding medication selection, dosing, and monitoring, and contribute to patient care discussions and treatment planning.
Conducting Medication Therapy Management
Medication therapy management (MTM) involves a comprehensive review of a patient’s medications to optimize therapy outcomes. Pharmacists assess medication regimens, identify potential medication-related problems, and make recommendations for therapy modifications or interventions to improve patient outcomes.
Managing Pharmacy Operations
Pharmacists are responsible for managing various aspects of pharmacy operations, including inventory management, quality control, and regulatory compliance. They ensure medications are stored properly, monitor medication expiry dates, and address any issues related to drug sourcing, storage, or dispensing.
Maintaining Patient Records
Pharmacists maintain accurate and confidential patient records, including medication profiles and documentation of medication interventions or counseling. They ensure that patient information is up-to-date and accessible to healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care.
Participating in Medication Safety Programs
Pharmacists actively participate in medication safety programs aimed at preventing medication errors and adverse drug events. They identify and report medication errors, implement preventive measures, and provide education and training on safe medication practices to other healthcare professionals and pharmacy staff.
Contributing to Research and Education
Pharmacists have opportunities to contribute to research and education initiatives. They may participate in research studies, collect and analyze data, and contribute to publications or presentations. Additionally, pharmacists often play a role in educating future pharmacists, serving as preceptors or instructors in pharmacy schools or residency programs.
Salary and Compensation
As mentioned earlier, the salary range for pharmacists can vary depending on various factors. Here is an overview of the salary and compensation aspects of a pharmacist career:
Average Pharmacist Salary
As of May 2020, the median annual wage for pharmacists in the United States was $128,710, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. However, it is important to note that this figure can vary based on factors such as experience, setting, geographic location, and additional certifications or advanced degrees.
Factors Affecting Salary
Several factors can affect a pharmacist’s salary. Experience plays a significant role, with more experienced pharmacists tending to earn higher salaries. The setting in which a pharmacist works also impacts salary, with pharmacists in hospitals or specialized fields often earning higher salaries compared to those in retail or community settings. Additional certifications, such as board certifications or specialized training, can also influence earning potential.
Salary Range by Experience and Setting
The salary range for pharmacists can vary based on experience and setting. Entry-level pharmacists typically earn lower salaries, ranging from $87,790 to $100,960. With experience, pharmacists can progress to mid-level positions, with salaries ranging from $100,960 to $135,120. Experienced pharmacists or those in specialized roles can earn higher salaries, with the range extending beyond $162,900.
Opportunities for Bonuses and Benefits
In addition to base salaries, pharmacists may have opportunities for bonuses and benefits. Bonuses can be based on factors such as meeting performance targets or working in high-demand areas. Benefits often include health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, and opportunities for continuing education and professional development.
Comparison with Other Healthcare Professions
Pharmacists generally have competitive salaries compared to other healthcare professions. The level of education and training required, as well as the responsibilities pharmacists hold, contribute to their earning potential. However, it is important to note that salary is just one aspect of job satisfaction, and pharmacists find fulfillment in other aspects of their work, such as patient care and contributing to public health.
Geographical Variations in Compensation
Compensation for pharmacists can vary based on geographic location. Factors such as cost of living, demand for pharmacists, and regional healthcare disparities can influence salary ranges. Higher-populated areas or regions with a shortage of pharmacists may offer more competitive salaries to attract qualified professionals.
Pharmacist Unionization and Collective Bargaining
Some pharmacists may choose to join unions or engage in collective bargaining to negotiate employment terms and conditions. Unionized pharmacists may have additional benefits and protections, such as standardized wage scales, improved working conditions, and stronger job security. Union representation can also provide a platform for pharmacists to advocate for their professional interests and contribute to the advancement of the field.
Job Market and Opportunities
The job outlook for pharmacists in the United States is generally positive. Here are some factors affecting the job market and opportunities for pharmacists:
Projected Growth of the Pharmacist Workforce
The demand for pharmacists is projected to grow in the coming years. Factors contributing to this growth include an aging population, increased chronic disease prevalence, and expanded healthcare services. Pharmacists are vital in managing medication therapy, optimizing patient outcomes, and ensuring safe medication use, making their expertise highly sought after.
Factors Affecting Job Outlook
Several factors can impact the job outlook for pharmacists. Competition for positions can be influenced by the number of pharmacy graduates, changes in healthcare policies, and economic factors. Demographic shifts, such as population growth and distribution, can also impact opportunities for pharmacists in specific regions or settings.
Demand for Specialty Pharmacy Services
The growing complexity of healthcare and the rise of specialty medications have increased the demand for pharmacy services in specialized areas. Specialty pharmacies, which focus on providing medications for complex or chronic conditions, require pharmacists with expertise in these specialized therapies. The demand for specialty pharmacy services offers opportunities for pharmacists to further specialize and advance their careers.
Opportunities in Rural and Underserved Areas
In rural or underserved areas, there may be a shortage of healthcare professionals, including pharmacists. These areas often face challenges in accessing quality healthcare services, including medication management. Pharmacists who are willing to work in these areas may find increased job opportunities and potentially unique career experiences.
Potential Impact of Automation and Technology
Advancements in automation and technology have the potential to impact the pharmacy profession. While automation can streamline certain tasks and improve efficiency, it may also affect the demand for certain roles within the profession. Pharmacists who adapt to and embrace technological advancements can position themselves for new opportunities and roles within the evolving healthcare landscape.
Job Prospects for Pharmacist Graduates
Although the job market for pharmacists is competitive, the demand for pharmacy services continues to grow. Graduates of Pharm.D. programs can find job prospects in various settings, including hospitals, retail pharmacies, clinics, and other healthcare organizations. Networking, gaining relevant experience during internships or rotations, and staying current with industry trends can increase job prospects for pharmacy graduates.
Career Advancement and Growth Potential
The pharmacy profession offers numerous opportunities for career advancement and growth. Pharmacists can pursue additional certifications or advanced degrees to specialize in particular areas of interest. Advanced practice roles, such as clinical pharmacy specialists or pharmacy managers, allow pharmacists to take on leadership positions and expand their scope of practice. Furthermore, pharmacists can contribute to research, education, or healthcare administration, opening doors to non-traditional career paths.
Challenges and Rewards in Pharmacy
Being a pharmacist comes with both challenges and rewards. Here are some of the common challenges and rewards in the field of pharmacy:
High Workload and Fast Paced Environment
Pharmacists often face a high workload in fast-paced environments, especially in settings like hospitals or retail pharmacies. Managing multiple responsibilities, such as dispensing medications, counseling patients, and conducting medication therapy management, requires strong organizational and time management skills. The ability to work efficiently and handle pressure is crucial in maintaining quality patient care.
Dealing with Insurance Companies and Prior Authorizations
Pharmacists frequently encounter challenges in navigating insurance coverage and prior authorizations. Processing insurance claims, ensuring formulary compliance, and obtaining prior authorizations for medications can be time-consuming and complex. Pharmacists must stay updated on insurance regulations and advocate for patient access to necessary medications.
Legal and Ethical Responsibilities
Pharmacists have legal and ethical responsibilities to ensure patient safety and comply with regulations. Handling controlled substances, protecting patient confidentiality, and adhering to professional standards are some of the legal and ethical considerations that pharmacists must navigate in their daily practice. Remaining vigilant and maintaining integrity are essential aspects of the profession.
Staying Current with Changing Treatment Guidelines
The field of pharmacy constantly evolves, with new medications, treatment guidelines, and evidence-based practices emerging. Pharmacists must continuously update their knowledge and skills to stay current with changing treatment guidelines. Keeping up with the latest research and guidelines requires a commitment to lifelong learning.
Making a Positive Impact on Patient Outcomes
One of the most rewarding aspects of being a pharmacist is the ability to make a positive impact on patient outcomes. Pharmacists play a vital role in medication management and patient care. From ensuring accurate medication dispensing to providing medication counseling and monitoring for adverse reactions, pharmacists contribute to improving patient health and well-being.
Career Stability and Job Security
The demand for pharmacists is expected to remain strong, providing a sense of career stability and job security. As the population continues to age and the need for medication management grows, pharmacists are essential in meeting healthcare demands. The skills and expertise of pharmacists are highly valued, offering a sense of job security in a changing healthcare landscape.
Contributing to Public Health
Pharmacists contribute to public health by promoting safe and effective medication use. Through patient education, medication therapy management, and participation in public health initiatives, pharmacists play a role in preventing medication errors, reducing medication-related complications, and improving overall population health. Pharmacists have the opportunity to positively impact the health of their communities.
Opportunities for Specialization and Clinical Practice
The field of pharmacy offers numerous opportunities for specialization and clinical practice. Pharmacists can pursue areas of interest or passion, such as geriatrics, oncology, or pediatrics, to focus their expertise on a specific patient population or disease state. Specialization allows pharmacists to make a significant impact in their chosen area of practice and offer specialized care to patients.
Professional Recognition and Respect
Pharmacists are recognized as essential healthcare professionals and are respected for their expertise and contributions to patient care. They collaborate with physicians and other healthcare professionals as valued members of the healthcare team. Pharmacists’ professional expertise and knowledge command respect from both colleagues and patients.
Flexible Work Schedules
Pharmacy offers flexibility in work schedules, with opportunities for part-time or variable-shift positions. This flexibility can be particularly beneficial for individuals seeking work-life balance or those with personal commitments outside of work. Pharmacists have the ability to choose from a variety of work settings and schedule options to suit their individual needs.
Conclusion
A career in pharmacy offers rewarding opportunities for those interested in healthcare. As a pharmacist, you play a critical role in ensuring the safe and effective use of medications, optimizing patient outcomes, and contributing to public health. The path to becoming a pharmacist involves completing a Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm.D.) program after earning a Bachelor’s degree and fulfilling prerequisite coursework. With a wide range of specializations available and a positive job outlook, pharmacists have opportunities for career advancement and growth. The challenges and rewards in pharmacy, along with competitive salaries and job stability, make it an appealing career path for those considering a profession in the United States.